Difference between revisions of "CPUProject"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
CPU project is one of the projects designed in department of computer engineering at TTU as a lab project. The main aims of this project are: | CPU project is one of the projects designed in department of computer engineering at TTU as a lab project. The main aims of this project are: | ||
| − | * Developing a generic CPU | + | * Developing a generic simple CPU |
* Writing a compiler for it | * Writing a compiler for it | ||
* Compiling GCC for this architecture | * Compiling GCC for this architecture | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | [[File:BlockDiagram.png|400px|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:BlockDiagram.png|400px|thumb|right|alt= text| Fig 1: System Block Diagram]] |
The architecture of this CPU is based on harvard architecture which has separate instruction and data memory. The instructions are assumed to be in the instruction memory before boot. | The architecture of this CPU is based on harvard architecture which has separate instruction and data memory. The instructions are assumed to be in the instruction memory before boot. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
Our CPU's instuction has 8 bit of upcode and one operand that can be as long as 32 bit. | Our CPU's instuction has 8 bit of upcode and one operand that can be as long as 32 bit. | ||
First 2 bits of OPcode are at the moment reserved. | First 2 bits of OPcode are at the moment reserved. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:instructionformat.png|400px|thumb|right |alt= text| Fig 2: Instruction fromat]] | ||
| + | |||
== Addressing Modes == | == Addressing Modes == | ||
The following Addressing modes are supported in out processor: | The following Addressing modes are supported in out processor: | ||
| Line 40: | Line 43: | ||
The following instrcutions designed for the CPU: | The following instrcutions designed for the CPU: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Table 1: Instruction Set | ||
|- | |- | ||
! !! Instruction !! Register Transfer Language !! OpCode !! DPU Command !! Data To DPU !! MemAddress !! Next PC | ! !! Instruction !! Register Transfer Language !! OpCode !! DPU Command !! Data To DPU !! MemAddress !! Next PC | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1|| Add_A_B || A <-- A + B || | + | | 1|| Add_A_B || A <-- A + B || 00 0000 || 00 000 0000 10 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2|| Add_A_Mem || A <-- A + Mem[Operand] || | + | | 2|| Add_A_Mem || A <-- A + Mem[Operand] || 00 0001 || 00 000 0000 00 || ---- || Operand || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 3|| Add_A_Dir || A <-- A + Operand || | + | | 3|| Add_A_Dir || A <-- A + Operand || 00 0010 || 00 000 0000 01 || Operand || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 4|| Sub_A_B || A <-- A - B || | + | | 4|| Sub_A_B || A <-- A - B || 00 0011 || 00 000 0001 10 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 5|| Sub_A_Mem || A <-- A - Mem[Operand] || | + | | 5|| Sub_A_Mem || A <-- A - Mem[Operand] || 00 0100 || 00 000 0001 00 || ---- || Operand || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 6|| Sub_A_Dir || A <-- A - Operand || | + | | 6|| Sub_A_Dir || A <-- A - Operand || 00 0101 || 00 000 0001 01 || Operand || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 7|| IncA || A <-- A + 1 || | + | | 7|| IncA || A <-- A + 1 || 00 0110 || 00 000 0000 11 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 8|| DecA || A <-- A - 1 || | + | | 8|| DecA || A <-- A - 1 || 00 0111 || 00 000 0001 11 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 9|| ShiftArithR || A <-- A(7) & A(7 downto 1) || | + | | 9|| ShiftArithR || A <-- A(7) & A(7 downto 1) || 00 1000 || 00 000 0111 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 10|| ShiftArithL || A <-- A(7) & A(5 downto 0)& '0' || | + | | 10|| ShiftArithL || A <-- A(7) & A(5 downto 0)& '0' || 00 1001 || 00 000 1000 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 11|| ShiftA_R || A <-- A(6 downto 0)& '0' || | + | | 11|| ShiftA_R || A <-- A(6 downto 0)& '0' || 00 1010 || 00 000 1010 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 12|| ShiftA_L || A <-- '0' & A(7 downto 1) || | + | | 12|| ShiftA_L || A <-- '0' & A(7 downto 1) || 00 1011 || 00 000 1011 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 13|| RRC || A <-- C & A(7 downto 1) ,C<-- A(0) || | + | | 13|| RRC || A <-- C & A(7 downto 1) ,C<-- A(0) || 00 1100 || 00 000 1110 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 14|| RLC || A <-- A(6 downto 0) & C ,C<-- A(7) || | + | | 14|| RLC || A <-- A(6 downto 0) & C ,C<-- A(7) || 00 1101 || 00 000 1111 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 15|| And_A_B || A <-- A and B || | + | | 15|| And_A_B || A <-- A and B || 00 1110 || 00 000 0100 10 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 16|| OR_A_B || A <-- A or B || | + | | 16|| OR_A_B || A <-- A or B || 00 1111 || 00 000 0101 10 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 17|| XOR_A_B || A <-- A xor B || | + | | 17|| XOR_A_B || A <-- A xor B || 01 0000 || 00 000 0110 10 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 18|| FlipA || A <-- not (A) || | + | | 18|| FlipA || A <-- not (A) || 01 0001 || 00 000 1100 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 19|| NegA || A <-- not(A) + 1 || | + | | 19|| NegA || A <-- not(A) + 1 || 01 0010 || 00 000 1001 00 || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 20|| Jmp || PC <-- Operand || | + | | 20|| Jmp || PC <-- Operand || 01 0011 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || Operand |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 21|| JmpZ || if Z = 1: PC <-- Operand || | + | | 21|| JmpZ || if Z = 1: PC <-- Operand || 01 0100 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || if Z=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 22|| JmpOV || if OV = 1: PC <-- Operand || | + | | 22|| JmpOV || if OV = 1: PC <-- Operand || 01 0101 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || if OV=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 23|| JmpC || if C = 1: PC <-- Operand || | + | | 23|| JmpC || if C = 1: PC <-- Operand || 01 0110 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || if C=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 24|| Jmp_rel || PC <-- PC + Operand || | + | | 24|| Jmp_rel || PC <-- PC + Operand || 01 0111 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC <-- PC + Operand |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 25|| JMPEQ || if EQ = 1: PC <-- Operand || | + | | 25|| JMPEQ || if EQ = 1: PC <-- Operand || 01 1000 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || if EQ=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 26|| ClearZ || Z <--- 0 || | + | | 26|| ClearZ || Z <--- 0 || 01 1001 || 00 001 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 27|| ClearOV || OV <--- 0 || | + | | 27|| ClearOV || OV <--- 0 || 01 1010 || 00 010 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 28|| ClearC || C <--- 0 || | + | | 28|| ClearC || C <--- 0 || 01 1011 || 00 100 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 29|| ClearACC || ACC <-- 0 || | + | | 29|| ClearACC || ACC <-- 0 || 01 1100 || 00 000 1101 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 30|| LoadPC || PC <---- A || | + | | 30|| LoadPC || PC <---- A || 01 1101 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || A |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 31|| SavePC || A <---- PC || | + | | 31|| SavePC || A <---- PC || 01 1110 || 00 000 0011 01 || PC || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 32|| Load_A_Mem || A <-- Mem[Operand] || | + | | 32|| Load_A_Mem || A <-- Mem[Operand] || 01 1111 || 00 000 0011 00 || ---- || Operand || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 33|| Store_A_Mem || Mem[Operand] <-- A || | + | | 33|| Store_A_Mem || Mem[Operand] <-- A || 10 0000 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || Operand || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 34|| Load_B_Dir || B <-- Operand || | + | | 34|| Load_B_Dir || B <-- Operand || 10 0001 || 01 000 0010 XX || Operand || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 35||Load_B_Mem || B <-- Mem[Operand] || | + | | 35||Load_B_Mem || B <-- Mem[Operand] || 10 0010 || 11 000 0010 XX || ---- || Operand || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 36||Load_A_B || A <-- B || | + | | 36||Load_A_B || A <-- B || ????? || 00 000 0011 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 37||Load_B_A || B <-- A | + | | 37||Load_B_A || B <-- A || ????? || 10 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 38||Load_Ind_A || A <-- M[A] || | + | | 38||Load_Ind_A || A <-- M[A] || ????? || 00 000 0011 00 || ---- || A || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 39|| PUSH || Mem [0 + SP] <--- A,SP <--- SP + 1 || | + | | 39|| PUSH || Mem [0 + SP] <--- A,SP <--- SP + 1 || 11 1100 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || SP || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 40|| POP || A <--- Mem [0 + SP - 1],SP <--- SP - 1 || | + | | 40|| POP || A <--- Mem [0 + SP - 1],SP <--- SP - 1 || 11 1101 || 00 000 0011 00 || ---- || SP - 1 || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 41|| NOP || NOP || | + | | 41|| NOP || NOP || 11 1110 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC_out+1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 42|| HALT || HALT || | + | | 42|| HALT || HALT || 11 1111 || 00 000 0010 XX || ---- || ---- || PC |
|} | |} | ||
=== Implementation of complex instructions=== | === Implementation of complex instructions=== | ||
| Line 160: | Line 164: | ||
== DataPath unit== | == DataPath unit== | ||
| − | [[File:DPU.png|350px|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:DPU.png|350px|thumb|right|alt= text| Fig 3: DPU block diagram]] |
| − | Datapath unit includes an Arithmatic Logical Unit (ALU), one Accumulator(ACC) and one general purpose register(Register B) and 2 multiplexers along with the flags. | + | Datapath unit includes an Arithmatic Logical Unit (ALU), one Accumulator(ACC) and one general purpose register(Register B) and 2 multiplexers along with the flags (see Fig. 3). |
The DPU command is formed as following: | The DPU command is formed as following: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! B_MUX !! | + | ! B_MUX !! SetFlags !! ALU command || ALU_MUX |
|- | |- | ||
| 2 bits || 3 bits || 4 bits || 2 bits | | 2 bits || 3 bits || 4 bits || 2 bits | ||
| Line 173: | Line 177: | ||
===ALU Multiplexer=== | ===ALU Multiplexer=== | ||
| − | The ALU multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table | + | The ALU multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table 2. |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | {| class="wikitable floatright" |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |+ Table 2: ALU Mux | ||
! !! command !! output | ! !! command !! output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 190: | Line 195: | ||
===B-Register Multiplexer=== | ===B-Register Multiplexer=== | ||
| − | The B-register multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table | + | The B-register multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table 3. |
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | {| class="wikitable floatright" |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |+ Table 3: Register B Mux | ||
! !! command !! output | ! !! command !! output | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 210: | Line 216: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |+ Table 4: ALU commands | ||
! !! Command !! Operation !! Description | ! !! Command !! Operation !! Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 247: | Line 254: | ||
===Flags=== | ===Flags=== | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable floatright" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" | + | |
|- | |- | ||
| + | |+ Table 5: DPU Flag | ||
! !! command !! FlagToClear | ! !! command !! FlagToClear | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 || 001 || Clear Z | | 1 || 001 || Clear Z | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2 || | + | | 2 || 010 || Clear OV |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 || 100 || Clear C | | 3 || 100 || Clear C | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | In DPU has the following flags: | ||
| + | * '''Zero Flag (Z)''': will be set if the result of the operation is zero | ||
| + | * '''Overflow Flag (OV)''': will be set if an overflow happens in signed operations (as an example if we have 8 bit addition of 82+91 the answer we expect is 173 but the result would be interpreted as -45). Overflow flag can be realized in the following way: | ||
| + | * '''Carry Flag (C)''': will be set if the unsigned addition or subtraction results in a carry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To clear flags,the SetFlag commands are used in DPU command (see table 5). | ||
| + | |||
== Instruction Memory (ROM) == | == Instruction Memory (ROM) == | ||
| − | Instruction memory is a read only memory that user will fill in the beginning. | + | Instruction memory is a read only memory that user will fill in the beginning. |
| + | entity InstMem is | ||
| + | generic (BitWidth: integer; | ||
| + | InstructionWidth: integer); | ||
| + | port ( address : in std_logic_vector(BitWidth-1 downto 0); | ||
| + | data : out std_logic_vector(InstructionWidth-1 downto 0) ); | ||
| + | end entity InstMem; | ||
| + | |||
| + | architecture behavioral of InstMem is | ||
| + | type mem is array ( 0 to 40) of std_logic_vector(InstructionWidth-1 downto 0); | ||
| + | constant my_InstMem : mem := ( | ||
| + | 0 => "0001110000000000000000000000000000011000", | ||
| + | 1 => "0000100100000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | 2 => "0000011000000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | 3 => "0000001100000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | 4 => "0011111000000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | ... | ||
| + | 37 => "0010000000000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | 38 => "0011110100000000000000000000000000000000", | ||
| + | 39 => "0000001000000000000000000000000000000011", | ||
| + | 40 => "0001010000000000000000000000000000000000" | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | begin | ||
| + | data <= my_InstMem(to_integer(unsigned(address))); | ||
| + | end architecture behavioral; | ||
| + | |||
== Data Memory == | == Data Memory == | ||
| − | [[File:DataMem.png|300px|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:DataMem.png|300px|thumb|right|alt= text| Fig 4: Data Memory block diagram]] |
| − | Data memory | + | Data memory is made out of blocks of 1024 registers. If user wants bigger size memory, it would be necessary to add more blocks. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Writing into data memory takes one clock cycle but readingf from it can be done instantly(or in reletively shorter time). So we can assume that if we issue address in one clock cycle, we can get the data in the same clock cycle. | Writing into data memory takes one clock cycle but readingf from it can be done instantly(or in reletively shorter time). So we can assume that if we issue address in one clock cycle, we can get the data in the same clock cycle. | ||
| + | There is a stack is at the top of data memory and its size is not restricted. Behavioural VHDL description of one instance of data memory is shown in the code below. | ||
| − | + | entity DATA_Mem is | |
| + | generic (BitWidth: integer); | ||
| + | port ( Address: in std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0); | ||
| + | Data_in: in std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0); | ||
| + | clk: in std_logic; | ||
| + | RW: in std_logic; | ||
| + | rst: in std_logic; | ||
| + | Data_Out: out std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0) | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | end DATA_Mem; | ||
| + | |||
| + | architecture beh of DATA_Mem is | ||
| + | type Mem_type is array (0 to (2**10)-1) of std_logic_vector(BitWidth-1 downto 0); | ||
| + | signal Mem : Mem_type; | ||
| + | begin | ||
| + | |||
| + | MemProcess: process(clk,rst) is | ||
| + | begin | ||
| + | if rst = '1' then | ||
| + | Mem<= ((others=> (others=>'0'))); | ||
| + | elsif rising_edge(clk) then | ||
| + | if RW = '1' then | ||
| + | Mem(to_integer(unsigned(Address))) <= Data_in; | ||
| + | end if; | ||
| + | end if; | ||
| + | end process MemProcess; | ||
| + | Data_Out <= Mem(to_integer(unsigned(Address))); | ||
| + | end beh; | ||
== Control unit== | == Control unit== | ||
| − | [[File:ControllerFSM.png|300px|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:ControllerFSM.png|300px|thumb|right|alt= text| Fig 5: Control unit FSM]] |
| − | [[File:InstDec.png|300px|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:InstDec.png|300px|thumb|right|alt= text| Fig 6: Control unit block diagram]] |
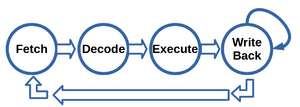
Control unit has four states: | Control unit has four states: | ||
| − | * '''Fetch''': fetches the instructions from instruction memory and loads it in Instruction Register (IR) | + | * '''Fetch''': fetches the instructions from instruction memory and loads it in Instruction Register (IR). DPU is IDLE. No Read from data memory. |
| − | * '''Decode''': decodes the information in IR | + | * '''Decode''': decodes the information in IR. DPU is IDLE. No Read from data memory. |
| − | * '''Execute''': if execution on DPU is needed the proper control signals would be provided, otherwise DPU will stay IDLE | + | * '''Execute''': if execution on DPU is needed the proper control signals would be provided, otherwise DPU will stay IDLE. Read from data memory performed if needed. |
* '''WriteBack''': in case there is a need to write a data into memory it will happen in this stage. All changes in Program Counter(PC) is happening here so all conditional and unconditional branching would be decided in this state. in case the instruction is HALT the PC would be frozen. | * '''WriteBack''': in case there is a need to write a data into memory it will happen in this stage. All changes in Program Counter(PC) is happening here so all conditional and unconditional branching would be decided in this state. in case the instruction is HALT the PC would be frozen. | ||
== Functional Testing == | == Functional Testing == | ||
| − | Following machine code program has been made to test functionality of all instructions. The test program doesnt cover all the cases but run through all the instructions. | + | Following machine code program has been made to test functionality of all instructions. The test program doesnt cover all the cases but run through all the instructions. |
| − | + | (at the moement not all the instructions are covered-12% missing) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | <source lang="javascript" collapse="true" first-line="2"> | ||
| + | Load_B_Dir "00011000" | ||
| + | OR_A_B | ||
| + | IncA | ||
| + | Sub_A_B | ||
| + | NOP | ||
| + | JmpC "00001000" | ||
| + | NOP | ||
| + | NOP | ||
| + | RRC | ||
| + | RLC | ||
| + | NOP | ||
| + | ClearC | ||
| + | Store_A_Mem "00010000" | ||
| + | PUSH | ||
| + | SavePC | ||
| + | PUSH | ||
| + | Jump "00010101" | ||
| + | POP | ||
| + | ShiftArithL | ||
| + | DecA | ||
| + | HALT | ||
| + | Load_A_Mem "00010000" | ||
| + | And_A_B | ||
| + | JmpZ "00011001" | ||
| + | NOP | ||
| + | ClearZ | ||
| + | Add_A_Mem "00010000" | ||
| + | Sub_A_Mem "00010000" | ||
| + | Add_A_B | ||
| + | Sub_A_Dir "00001100" | ||
| + | FlipA | ||
| + | XOR_A_B | ||
| + | NegA | ||
| + | ShiftArithR | ||
| + | ShiftA_L | ||
| + | ShiftA_R | ||
| + | ClearACC | ||
| + | POP | ||
| + | Add_A_Dir "00000011" | ||
| + | LoadPC | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 299: | Line 396: | ||
The following are the future plans for CPU: | The following are the future plans for CPU: | ||
* Implementing load_A_B and Load_B_A | * Implementing load_A_B and Load_B_A | ||
| − | |||
* Fixing the size of data memory as a memory block and do a memory map to multiple instances of the block | * Fixing the size of data memory as a memory block and do a memory map to multiple instances of the block | ||
* Adding indexed data addressing: A <--- M[A] | * Adding indexed data addressing: A <--- M[A] | ||
| Line 305: | Line 401: | ||
* implement barrel shift on acc | * implement barrel shift on acc | ||
* Adding I/O | * Adding I/O | ||
| + | ** first try would be Input and Output registers | ||
**wishbone bus maybe? | **wishbone bus maybe? | ||
* Adding interupts | * Adding interupts | ||
| Line 324: | Line 421: | ||
InstructionOpCode = { | InstructionOpCode = { | ||
| − | 'Add_A_B': " | + | 'Add_A_B': " ", |
| − | 'Add_A_Mem': " | + | 'Add_A_Mem': " ", |
| − | 'Add_A_Dir': " | + | 'Add_A_Dir': " ", |
| − | 'Sub_A_B': " | + | 'Sub_A_B': " ", |
| − | 'Sub_A_Mem': " | + | 'Sub_A_Mem': " ", |
| − | 'Sub_A_Dir': " | + | 'Sub_A_Dir': " ", |
| − | 'IncA': " | + | 'IncA': " ", |
| − | 'DecA': " | + | 'DecA': " ", |
| − | 'And_A_B': " | + | 'And_A_B': " ", |
| − | 'OR_A_B': " | + | 'OR_A_B': " ", |
| − | 'XOR_A_B': " | + | 'XOR_A_B': " ", |
| − | 'FlipA': " | + | 'FlipA': " ", |
| − | 'NegA': " | + | 'NegA': " ", |
| − | 'Jump': " | + | 'Jump': " ", |
| − | 'JmpZ': " | + | 'JmpZ': " ", |
| − | 'JmpOV': " | + | 'JmpOV': " ", |
| − | 'Jmp_rel': " | + | 'Jmp_rel': " ", |
| − | 'JMPEQ': " | + | 'JMPEQ': " ", |
| − | 'ClearZ': " | + | 'ClearZ': " ", |
| − | 'ClearOV': " | + | 'ClearOV': " ", |
| − | 'LoadPC': " | + | 'LoadPC': " ", |
| − | 'SavePC': " | + | 'SavePC': " ", |
| − | 'ShiftArithR': " | + | 'ShiftArithR': " ", |
| − | 'ShiftArithL': " | + | 'ShiftArithL': " ", |
| − | 'ShiftA_R': " | + | 'ShiftA_R': " ", |
| − | 'ShiftA_L': " | + | 'ShiftA_L': " ", |
| − | 'Load_A_Mem': " | + | 'Load_A_Mem': " ", |
| − | 'Store_A_Mem': " | + | 'Store_A_Mem': " ", |
| − | 'Load_B_Dir': " | + | 'Load_B_Dir': " ", |
| − | 'Load_B_Mem': " | + | 'Load_B_Mem': " ", |
| − | 'JmpC': " | + | 'JmpC': " ", |
| − | 'ClearC': " | + | 'ClearC': " ", |
| − | 'ClearACC': " | + | 'ClearACC': " ", |
| − | 'RRC': " | + | 'RRC': " ", |
| − | 'RLC': " | + | 'RLC': " ", |
| − | 'PUSH': " | + | 'PUSH': " ", |
| − | 'POP': " | + | 'POP': " ", |
| − | 'NOP': " | + | 'NOP': " ", |
| − | 'HALT': " | + | 'HALT': " ", |
} | } | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 7 December 2014
CPU project is one of the projects designed in department of computer engineering at TTU as a lab project. The main aims of this project are:
- Developing a generic simple CPU
- Writing a compiler for it
- Compiling GCC for this architecture
- Booting a lightweight linux on it
Contents
CPU Design
Functionality Requirements
The CPU is supposed to be able to perform the following operations:
- Addition/Subtraction
- Increment/Decrement
- Arithmetic and Logical Shift and Rotate through carry
- Bitwise AND, OR, XOR and NOT
- Negation
- Load/Store
- Unconditional Branch (jump)
- Branch if zero / Branch if Overflow / Branch if Carry
- Clear Registers/Flags
- PUSH / POP
- NOP/HALT
It can use these operations to build more sophisticated operations later.
Architecture
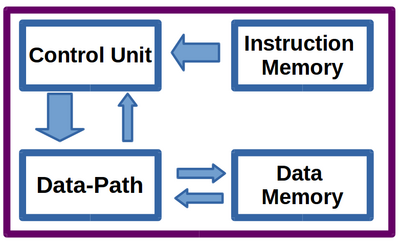
The architecture of this CPU is based on harvard architecture which has separate instruction and data memory. The instructions are assumed to be in the instruction memory before boot.
Instruction Format
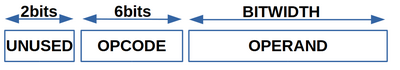
Our CPU's instuction has 8 bit of upcode and one operand that can be as long as 32 bit. First 2 bits of OPcode are at the moment reserved.
Addressing Modes
The following Addressing modes are supported in out processor:
- direct: program counter jumps to an address directly provided to it through instruction's operand
- relative: the program counter will jump to a location reletive to its current location
- indirect: program counter will jump to an address stored in a memory location
- register: program counter will jump to an address stored in a register
- indexed: program counter will jump to an address stored in the memory with address stored in a register
Instruction Set (IS)
The following instrcutions designed for the CPU:
| Instruction | Register Transfer Language | OpCode | DPU Command | Data To DPU | MemAddress | Next PC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add_A_B | A <-- A + B | 00 0000 | 00 000 0000 10 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 2 | Add_A_Mem | A <-- A + Mem[Operand] | 00 0001 | 00 000 0000 00 | ---- | Operand | PC_out+1 |
| 3 | Add_A_Dir | A <-- A + Operand | 00 0010 | 00 000 0000 01 | Operand | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 4 | Sub_A_B | A <-- A - B | 00 0011 | 00 000 0001 10 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 5 | Sub_A_Mem | A <-- A - Mem[Operand] | 00 0100 | 00 000 0001 00 | ---- | Operand | PC_out+1 |
| 6 | Sub_A_Dir | A <-- A - Operand | 00 0101 | 00 000 0001 01 | Operand | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 7 | IncA | A <-- A + 1 | 00 0110 | 00 000 0000 11 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 8 | DecA | A <-- A - 1 | 00 0111 | 00 000 0001 11 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 9 | ShiftArithR | A <-- A(7) & A(7 downto 1) | 00 1000 | 00 000 0111 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 10 | ShiftArithL | A <-- A(7) & A(5 downto 0)& '0' | 00 1001 | 00 000 1000 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 11 | ShiftA_R | A <-- A(6 downto 0)& '0' | 00 1010 | 00 000 1010 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 12 | ShiftA_L | A <-- '0' & A(7 downto 1) | 00 1011 | 00 000 1011 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 13 | RRC | A <-- C & A(7 downto 1) ,C<-- A(0) | 00 1100 | 00 000 1110 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 14 | RLC | A <-- A(6 downto 0) & C ,C<-- A(7) | 00 1101 | 00 000 1111 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 15 | And_A_B | A <-- A and B | 00 1110 | 00 000 0100 10 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 16 | OR_A_B | A <-- A or B | 00 1111 | 00 000 0101 10 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 17 | XOR_A_B | A <-- A xor B | 01 0000 | 00 000 0110 10 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 18 | FlipA | A <-- not (A) | 01 0001 | 00 000 1100 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 19 | NegA | A <-- not(A) + 1 | 01 0010 | 00 000 1001 00 | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 20 | Jmp | PC <-- Operand | 01 0011 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | Operand |
| 21 | JmpZ | if Z = 1: PC <-- Operand | 01 0100 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | if Z=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
| 22 | JmpOV | if OV = 1: PC <-- Operand | 01 0101 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | if OV=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
| 23 | JmpC | if C = 1: PC <-- Operand | 01 0110 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | if C=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
| 24 | Jmp_rel | PC <-- PC + Operand | 01 0111 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC <-- PC + Operand |
| 25 | JMPEQ | if EQ = 1: PC <-- Operand | 01 1000 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | if EQ=1 then Operand else PC_out+1 |
| 26 | ClearZ | Z <--- 0 | 01 1001 | 00 001 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 27 | ClearOV | OV <--- 0 | 01 1010 | 00 010 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 28 | ClearC | C <--- 0 | 01 1011 | 00 100 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 29 | ClearACC | ACC <-- 0 | 01 1100 | 00 000 1101 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 30 | LoadPC | PC <---- A | 01 1101 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | A |
| 31 | SavePC | A <---- PC | 01 1110 | 00 000 0011 01 | PC | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 32 | Load_A_Mem | A <-- Mem[Operand] | 01 1111 | 00 000 0011 00 | ---- | Operand | PC_out+1 |
| 33 | Store_A_Mem | Mem[Operand] <-- A | 10 0000 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | Operand | PC_out+1 |
| 34 | Load_B_Dir | B <-- Operand | 10 0001 | 01 000 0010 XX | Operand | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 35 | Load_B_Mem | B <-- Mem[Operand] | 10 0010 | 11 000 0010 XX | ---- | Operand | PC_out+1 |
| 36 | Load_A_B | A <-- B | ????? | 00 000 0011 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 37 | Load_B_A | B <-- A | ????? | 10 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 38 | Load_Ind_A | A <-- M[A] | ????? | 00 000 0011 00 | ---- | A | PC_out+1 |
| 39 | PUSH | Mem [0 + SP] <--- A,SP <--- SP + 1 | 11 1100 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | SP | PC_out+1 |
| 40 | POP | A <--- Mem [0 + SP - 1],SP <--- SP - 1 | 11 1101 | 00 000 0011 00 | ---- | SP - 1 | PC_out+1 |
| 41 | NOP | NOP | 11 1110 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC_out+1 |
| 42 | HALT | HALT | 11 1111 | 00 000 0010 XX | ---- | ---- | PC |
Implementation of complex instructions
the follwoing instructions can be also implemented with the ones in IS:
- Call "function_name":
PUSH SavePC Push Jmp "function address" POP
- Return:
POP Add_A_Dir 4 LoadPC
- IndJMP "MemAddress":
PUSH Load_A_Mem "MemAddress" LoadPC
Note: its important to POP back the ACC value on the jump destination.
- JmpB:
PUSH Load_A_B LoadPC
Note: its important to POP back the ACC value on the jump destination.
- JmpIndx:
PUSH Load_Ind_A LoadPC
Note: its important to POP back the ACC value on the jump destination.
DataPath unit
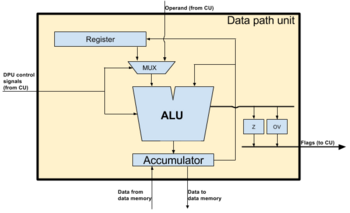
Datapath unit includes an Arithmatic Logical Unit (ALU), one Accumulator(ACC) and one general purpose register(Register B) and 2 multiplexers along with the flags (see Fig. 3). The DPU command is formed as following:
| B_MUX | SetFlags | ALU command | ALU_MUX |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 bits | 3 bits | 4 bits | 2 bits |
ALU Multiplexer
The ALU multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table 2.
| command | output | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00 | MemDATA |
| 2 | 01 | ControlDATa |
| 3 | 10 | B |
| 4 | 11 | 1 |
B-Register Multiplexer
The B-register multiplexer chooses the inputs according to the table 3.
| command | output | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 00 | B |
| 2 | 01 | ControlDATa |
| 3 | 10 | ALUResult |
| 4 | 11 | MemDATA |
ALU
The ALU covers the following operations:
| Command | Operation | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0000 | A + B | Addition |
| 2 | 0001 | A - B | |
| 3 | 0010 | A | Bypass A |
| 4 | 0011 | B | Bypass B |
| 5 | 0100 | A AND B | bitwise And |
| 6 | 0101 | A OR B | bitwise OR |
| 7 | 0110 | A XOR B | bitwise XOR |
| 8 | 0111 | '0' & A(BITWIDTH-1 DOWNTO 1) | Logical Shift Right |
| 9 | 1000 | A(BITWIDTH-2 DOWNTO 0) & '0' | Logical Shift Left |
| 10 | 1001 | NOT(A) + 1 | Negation |
| 11 | 1010 | A(BITWIDTH-1) & A(BITWIDTH-1 DOWNTO 1) | Arithmetic Shift Right |
| 12 | 1011 | A(BITWIDTH-1) & A(BITWIDTH-3 downto 0)& A(0) | Arithmetic Shift Left |
| 13 | 1100 | NOT(A) | Flip |
| 14 | 1101 | 0 | Clear A |
| 15 | 1110 | Cflag & A(BITWIDTH-1 downto 1) | Rotate Right Through Carry |
| 16 | 1111 | A(BITWIDTH-2 downto 0)& Cflag | Rotate Left Through Carry |
For addition/subtraction a ripple carry model is made out of chain of full adders.
Flags
| command | FlagToClear | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 001 | Clear Z |
| 2 | 010 | Clear OV |
| 3 | 100 | Clear C |
In DPU has the following flags:
- Zero Flag (Z): will be set if the result of the operation is zero
- Overflow Flag (OV): will be set if an overflow happens in signed operations (as an example if we have 8 bit addition of 82+91 the answer we expect is 173 but the result would be interpreted as -45). Overflow flag can be realized in the following way:
- Carry Flag (C): will be set if the unsigned addition or subtraction results in a carry.
To clear flags,the SetFlag commands are used in DPU command (see table 5).
Instruction Memory (ROM)
Instruction memory is a read only memory that user will fill in the beginning.
entity InstMem is
generic (BitWidth: integer;
InstructionWidth: integer);
port ( address : in std_logic_vector(BitWidth-1 downto 0);
data : out std_logic_vector(InstructionWidth-1 downto 0) );
end entity InstMem;
architecture behavioral of InstMem is
type mem is array ( 0 to 40) of std_logic_vector(InstructionWidth-1 downto 0);
constant my_InstMem : mem := (
0 => "0001110000000000000000000000000000011000",
1 => "0000100100000000000000000000000000000000",
2 => "0000011000000000000000000000000000000000",
3 => "0000001100000000000000000000000000000000",
4 => "0011111000000000000000000000000000000000",
...
37 => "0010000000000000000000000000000000000000",
38 => "0011110100000000000000000000000000000000",
39 => "0000001000000000000000000000000000000011",
40 => "0001010000000000000000000000000000000000"
);
begin
data <= my_InstMem(to_integer(unsigned(address)));
end architecture behavioral;
Data Memory
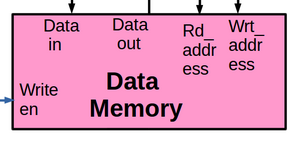
Data memory is made out of blocks of 1024 registers. If user wants bigger size memory, it would be necessary to add more blocks. Writing into data memory takes one clock cycle but readingf from it can be done instantly(or in reletively shorter time). So we can assume that if we issue address in one clock cycle, we can get the data in the same clock cycle. There is a stack is at the top of data memory and its size is not restricted. Behavioural VHDL description of one instance of data memory is shown in the code below.
entity DATA_Mem is
generic (BitWidth: integer);
port ( Address: in std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0);
Data_in: in std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0);
clk: in std_logic;
RW: in std_logic;
rst: in std_logic;
Data_Out: out std_logic_vector (BitWidth-1 downto 0)
);
end DATA_Mem;
architecture beh of DATA_Mem is
type Mem_type is array (0 to (2**10)-1) of std_logic_vector(BitWidth-1 downto 0);
signal Mem : Mem_type;
begin
MemProcess: process(clk,rst) is
begin
if rst = '1' then
Mem<= ((others=> (others=>'0')));
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if RW = '1' then
Mem(to_integer(unsigned(Address))) <= Data_in;
end if;
end if;
end process MemProcess;
Data_Out <= Mem(to_integer(unsigned(Address)));
end beh;
Control unit
Control unit has four states:
- Fetch: fetches the instructions from instruction memory and loads it in Instruction Register (IR). DPU is IDLE. No Read from data memory.
- Decode: decodes the information in IR. DPU is IDLE. No Read from data memory.
- Execute: if execution on DPU is needed the proper control signals would be provided, otherwise DPU will stay IDLE. Read from data memory performed if needed.
- WriteBack: in case there is a need to write a data into memory it will happen in this stage. All changes in Program Counter(PC) is happening here so all conditional and unconditional branching would be decided in this state. in case the instruction is HALT the PC would be frozen.
Functional Testing
Following machine code program has been made to test functionality of all instructions. The test program doesnt cover all the cases but run through all the instructions. (at the moement not all the instructions are covered-12% missing)
Load_B_Dir "00011000"
OR_A_B
IncA
Sub_A_B
NOP
JmpC "00001000"
NOP
NOP
RRC
RLC
NOP
ClearC
Store_A_Mem "00010000"
PUSH
SavePC
PUSH
Jump "00010101"
POP
ShiftArithL
DecA
HALT
Load_A_Mem "00010000"
And_A_B
JmpZ "00011001"
NOP
ClearZ
Add_A_Mem "00010000"
Sub_A_Mem "00010000"
Add_A_B
Sub_A_Dir "00001100"
FlipA
XOR_A_B
NegA
ShiftArithR
ShiftA_L
ShiftA_R
ClearACC
POP
Add_A_Dir "00000011"
LoadPC
Future plans
The following are the future plans for CPU:
- Implementing load_A_B and Load_B_A
- Fixing the size of data memory as a memory block and do a memory map to multiple instances of the block
- Adding indexed data addressing: A <--- M[A]
- Adding indexed instruction addressing: PC <--- M[A]
- implement barrel shift on acc
- Adding I/O
- first try would be Input and Output registers
- wishbone bus maybe?
- Adding interupts
- Pipelining
- Branch prediction
- Synthesis and FPGA implementation
- VGA controller?
- UART implementation
- implementation of Timers/Counters and peripherals
- Direct Memory Access (DMA)
Assembler
Python Assembly translator
A simple assembly translator was designed to make debugging process faster. Here you can see 32 bit version of the code:
import re
InstructionOpCode = {
'Add_A_B': " ",
'Add_A_Mem': " ",
'Add_A_Dir': " ",
'Sub_A_B': " ",
'Sub_A_Mem': " ",
'Sub_A_Dir': " ",
'IncA': " ",
'DecA': " ",
'And_A_B': " ",
'OR_A_B': " ",
'XOR_A_B': " ",
'FlipA': " ",
'NegA': " ",
'Jump': " ",
'JmpZ': " ",
'JmpOV': " ",
'Jmp_rel': " ",
'JMPEQ': " ",
'ClearZ': " ",
'ClearOV': " ",
'LoadPC': " ",
'SavePC': " ",
'ShiftArithR': " ",
'ShiftArithL': " ",
'ShiftA_R': " ",
'ShiftA_L': " ",
'Load_A_Mem': " ",
'Store_A_Mem': " ",
'Load_B_Dir': " ",
'Load_B_Mem': " ",
'JmpC': " ",
'ClearC': " ",
'ClearACC': " ",
'RRC': " ",
'RLC': " ",
'PUSH': " ",
'POP': " ",
'NOP': " ",
'HALT': " ",
}
AssemblyFile = open('Assembly.txt', 'r+')
MachineCodeFile = open('MachineCode.txt', 'w')
counter=0
for line in AssemblyFile:
for key in InstructionOpCode:
if key in line:
operand= "00000000"
if "Mem" in line:
operand = re.findall(r'\d+',line)[0]
elif "Jmp" in line:
operand = re.findall(r'\d+',line)[0]
elif "Dir" in line:
operand = re.findall(r'\d+',line)[0]
operand = "00000000"+"00000000"+"00000000"+ operand
MachineCodeFile.write(str(counter)+ " => "+ "\"00"+InstructionOpCode[key]+operand+'\",'+'\n')
counter +=1
MachineCodeFile.close()
AssemblyFile.close()
Java Assembler